Java constructors are the methods which are used to initialize objects. Constructor method has the same name as that of class, they are called or invoked when an object of class is created and can't be called explicitly. Attributes of an object may be available when creating objects if no attribute is available then default constructor is called, also some of the attributes may be known initially. It is optional to write constructor method in a class but due to their utility they are used.


When cpp object is created default constructor is called and when java object is created constructor with argument is called, setName method is used to set 'name' attribute of language, getName method prints language name.
Constructor chaining occurs when a class inherits another class i.e. in inheritance, as in inheritance sub class inherits the properties of super class. Both the super and sub class may have constructor methods, when an object of sub class is created it's constructor is invoked it initializes sub class attributes, now super class constructor needs to be invoked, to achieve this java provides a super keyword through which we can pass arguments to super class constructor. For more understanding see constructor chaining example:
class GrandParent {
Constructor method doesn't specify a return type, they return instance of class itself.
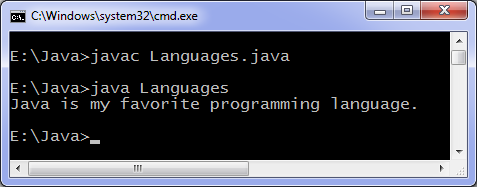
Java constructor example
class Programming {
//constructor method
Programming() {
System.out.println("Constructor method called.");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Programming object = new Programming();
//creating object
}
}
Output of program:
This code is the simplest example of constructor, we create class Programming and create an object, constructor is called when object is created. As you can see in output "Constructor method called." is printed.
Like other methods in java constructor can be overloaded i.e. we can create as many constructors in our class as desired. Number of constructors depends on the information about attributes of an object we have while creating objects. See constructor overloading example:
class Language {
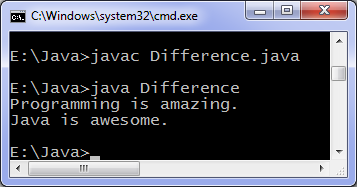
Java constructor overloading
Like other methods in java constructor can be overloaded i.e. we can create as many constructors in our class as desired. Number of constructors depends on the information about attributes of an object we have while creating objects. See constructor overloading example:
class Language {
String name;
Language() {
System.out.println("Constructor method called.");
}
Language(String t) {
name = t;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Language cpp = new Language();
Language java = new Language("Java");
cpp.setName("C++");
java.getName();
cpp.getName();
}
void setName(String t) {
name = t;
}
void getName() {
System.out.println("Language name: " + name);
}
}
Output of program:
When cpp object is created default constructor is called and when java object is created constructor with argument is called, setName method is used to set 'name' attribute of language, getName method prints language name.
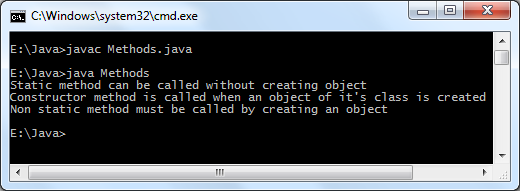
Java constructor chaining
Constructor chaining occurs when a class inherits another class i.e. in inheritance, as in inheritance sub class inherits the properties of super class. Both the super and sub class may have constructor methods, when an object of sub class is created it's constructor is invoked it initializes sub class attributes, now super class constructor needs to be invoked, to achieve this java provides a super keyword through which we can pass arguments to super class constructor. For more understanding see constructor chaining example:
class GrandParent {
int a;
GrandParent(int a) {
this.a = a;
}
}
class Parent extends GrandParent {
int b;
Parent(int a, int b) {
super(a);
this.b = b;
}
void show() {
System.out.println("GrandParent's a = " + a);
System.out.println("Parent's b = " + b);
}
}
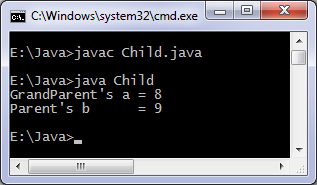
class Child {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Parent object = new Parent(8, 9);
object.show();
}
}
Output of program:

Constructor method doesn't specify a return type, they return instance of class itself.