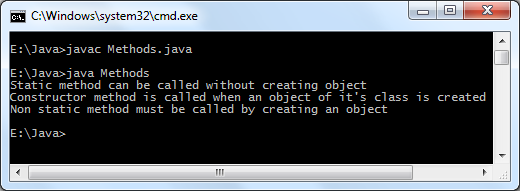
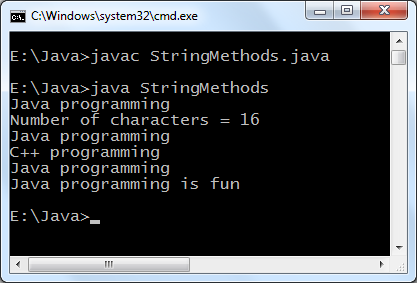
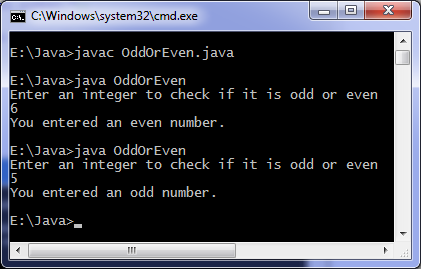
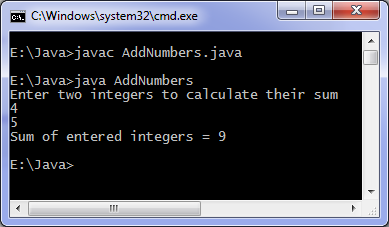
Java programming language offers a block known as static which is executed before main method executes. Below is the simplest example to understand functioning of static block later we see a practical use of static block.
Output of progam:

Static block can be used to check conditions before execution of main begin, Suppose we have developed an application which runs only on Windows operating system then we need to check what operating system is installed on user machine. In our java code we check what operating system user is using if user is using operating system other than "Windows" then the program terminates.
Java static block program
class StaticBlock {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Main method is executed.");
}
static {
System.out.println("Static block is executed before main method.");
}
}Output of progam:

Static block can be used to check conditions before execution of main begin, Suppose we have developed an application which runs only on Windows operating system then we need to check what operating system is installed on user machine. In our java code we check what operating system user is using if user is using operating system other than "Windows" then the program terminates.
class StaticBlock {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("You are using Windows_NT operating system.");
}
static {
String os = System.getenv("OS");
if (os.equals("Windows_NT") != true) {
System.exit(1);
}
}
}
We are using getenv method of System class which returns value of environment variable name of which is passed an as argument to it. Windows_NT is a family of operating systems which includes Windows XP, Vista, 7, 8 and others.
Output of program on Windows 7: